In general, flow measurement is the quantification of the movement of fluids. The flow can be indicated in several ways such as velocity, flow volume or mass flow rate. The flow volume is typically specified in millilitre or litre per period, whereas the mass flow volume is given in grams or kilograms per period.
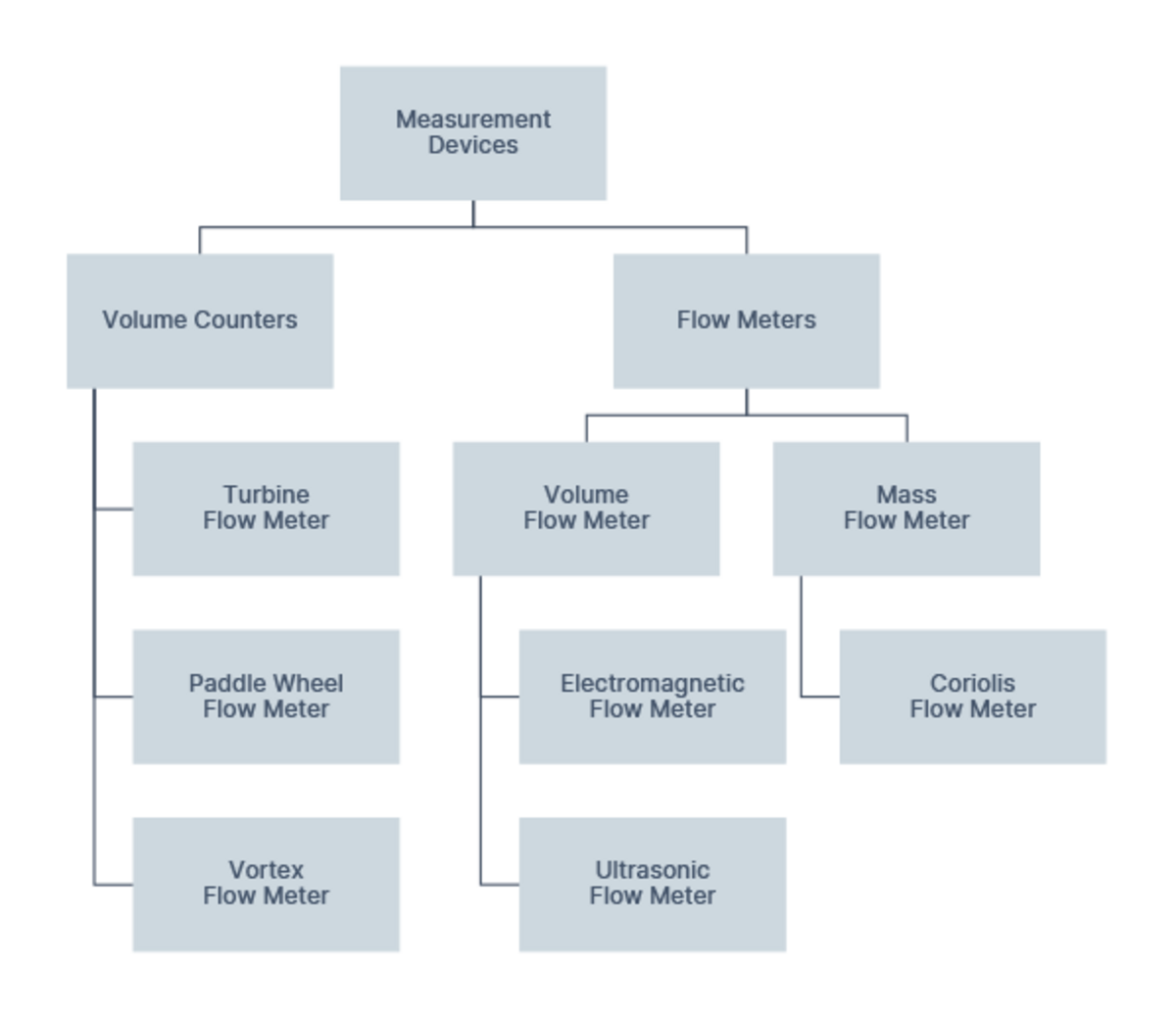
In order to measure the flow, volume counters or flow meters are used.
Despite their similarity, the terms ‘counter’ and ‘flow meter’ do not refer to the same thing: ‘Counting’ describes the recording of a quantity without any reference to a period of time, whereas ‘measuring’ defines the recording of the quantity per a defined period of time. Thus, for example, volume counters indicate litres, whereas flow meters measure in millilitres per minute.
For counting the flow volume a number of devices, such as a turbine flow meter, paddle wheel flow meter and vortex flow meters are available.
For measuring the flow volume, volume and mass flow meters are used such as electromagnetic flow meters, Coriolis flow meter, and ultrasonic flow meters.
All measurement devices, counters and flow meters, are influenced by certain ambient conditions as well as the characteristic of the liquid. So far, there is no ready-to-use solution on the market. The measurement device must fit to the application and the environment.